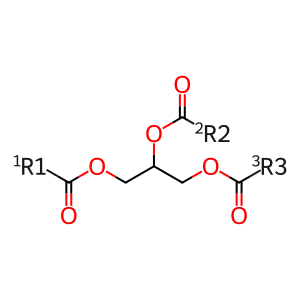
Reaction: FITM1, FITM2 bind TAGs
- in pathway: Lipid particle organization
Lipid droplets (LDs) are cytosolic structures found in cells of all eukaryotes, comprising a monolayer of phospholipids surrounding a core of uncharged lipids such as triglyceride (TAG) and sterol esters. They play an important role in both cellular physiology and disease. LD formation involves the partitioning of neutral lipids from their site of synthesis at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the cytosol. The fat storage-inducing transmembrane proteins 1 and 2 (FITM1 and FITM2) belong to an evolutionarily-conserved gene family which mediates LD formation (Kadereit et al. 2008, Gross et al. 2011). FITM1 and FITM2 are ER membrane associated proteins that mediate binding and partitioning of TAGs into LDs (Gross et al. 2011, Miranda et al. 2014). In mammals, FITM1 is expressed primarily in skeletal muscle whereas FITM2 is expressed primarily in adipose tissue, suggesting these proteins may have unique functions (Gross et al. 2011).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
TAG [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8857686
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
triglyceride
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8857686