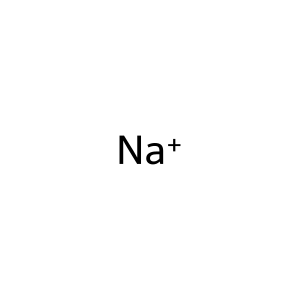Reaction: MFSD2A transports LPC from extracellular region to plasma membrane
- in pathway: Synthesis of PC
Sodium-dependent lysophosphatidylcholine symporter 1 (MFSD2A, aka NLS1) plays an essential role in blood-brain barrier (BBB) formation and function and transports LPC into the brain via a flipping motion (Nguyen et al. 2014, Guemez-Gamboa et al. 2015, Quek et al. 2016). LPCs are synthesised by the liver, circulate bound to albumin and serve as the chemical carrier for DHA uptake via MFSD2A. LPC can contain docosahexanoic acid (DHA), the most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in brain. Despite large DHA content in phospholipids, the brain does not synthesise it. MFSD2A is highly enriched in cerebral vasculature, where it is exclusively found in BBB endothelium.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
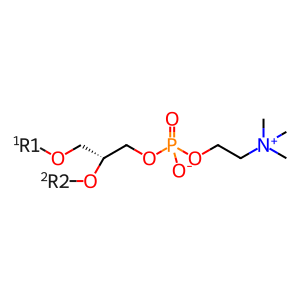
LPC (22:6) [cytosol]
Na+ [cytosol]
LPC (22:6) [extracellular region]
Na+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8865637
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
lysophosphatidylcholine 22:6
sodium(1+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
lysophosphatidylcholine 22:6
sodium(1+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8865637