Reaction: CCPs deglutamylate tubulin
Cytosolic carboxypeptidases (CCPs) catalyze the removal of glutamate residues from the C-terminal tails of both alpha- and beta-tubulin. These glutamate residues are either enzymatically added in the polyglutamylation reaction, or gene-encoded glutamate residues are removed from alpha-tubulin after detyrosination to generate delta2-tubulin (Kimura et al. 2010, Rogowski et al. 2010). CCPs are members of the MC clan, M14 family, subfamily M14D of metallopeptidases (Kalinina et al. 2007, Rodriguez de la Vega et al. 2007). Mouse Ccp1, 2, 3, 4, and 6 are functionally homologous and remove linearly added glutamates from tubulin (alpha-peptide bonds), while Ccp5 specifically removes branching-point glutamates (gamma-peptide bonds) which are generated as first step of the polyglutamylation reaction (Rogowski et al. 2010; Tort et al. 2014). The catalytic activities of the human proteins are inferred from the properties of their mouse homologues and limited studies of human proteins expressed in cultured cells (Rogowski et al. 2010). In this event polyglutamylation is arbitrarily shown on only one tubulin protofilament within the polyglutamylated microtubule.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
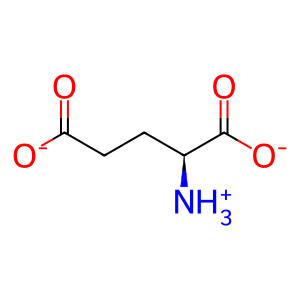
L-Glu [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8866105
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
L-glutamate(1-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8866105