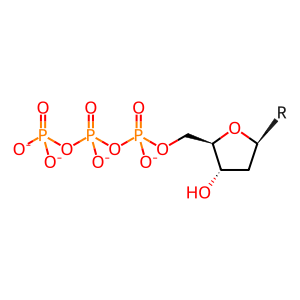
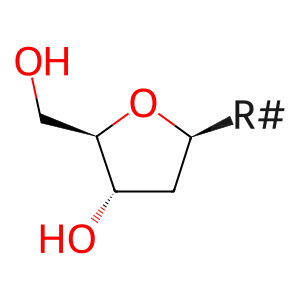
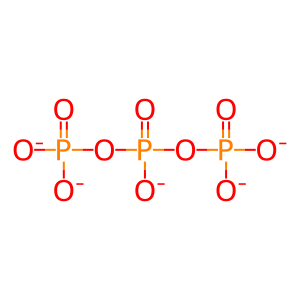
Reaction: SAMHD1:Zn2+ tetramer hydrolyzes dNTP to nucleoside and triphosphate
- in pathway: Nucleotide catabolism
SAMHD1:Zn2+ tetramer (Deoxynucleoside triphosphate triphosphohydrolase SAMHD1, also known as SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of dNTPs (2'-deoxynucleoside 5'-triphosphates) to form 2'-deoxynucleosides and PPPi (triphosphate) (Goldstone et al. 2011; Powell et al. 2011). The active form of the enzyme is a tetramer with one Zn2+ ion associated with each monomer subunit (Yan et al. 2013; Zhu et al. 2013) localized in the nucleus (Franzolin et al. 2013; Rice et al. 2009). The enzyme is activated by dGTP (Powell et al. 2011).
SAMHD1 activity may play a role in regulating the size of the nuclear pools of dNTPs and dissipating these pools at the end of the S phase of the cell cycle (Franzolin et al. 2013) and it may play a role as well in regulating cellular antiviral responses (Goldstone et al. 2011; Rice et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
2'-deoxynucleoside [nucleoplasm]
H+ [nucleoplasm]
PPPi [nucleoplasm]
H2O [nucleoplasm]
dNTP(4-) [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8866601
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
2'-deoxyribonucleoside 5'-triphosphate(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
2'-deoxyribonucleoside
hydron
triphosphate(5-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8866601