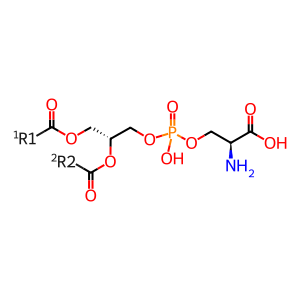
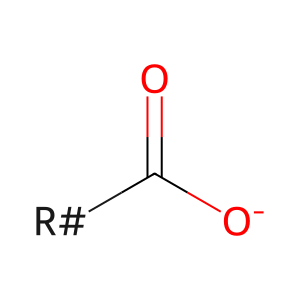
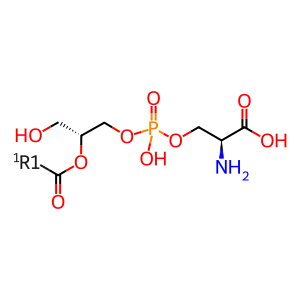
Reaction: PLA1A hydrolyses PS to 2-acyl LPS
- in pathway: Acyl chain remodelling of PS
Phospholipase A1 member A (PLA1A, aka PS-PLA1) is a widely expressed, extracellular protein belonging to the pancreatic lipase family. Phospholipases are conserved in a wide range of organisms. PLA1A specifically hydrolyses PS to produce its corresponding lysophospholipid 2-acyl LPS. Lysophospholipids in general can act as lipid mediators with multiple biological functions so PLA1A could play an important role in mediating 2-acyl LPS production (Nagai et al. 1999, Aoki et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
LCFA(-) [plasma membrane]
2-acyl LPS [plasma membrane]
H2O [extracellular region]
PS [plasma membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8869425
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
3-sn-phosphatidyl-L-serine
Reaction output - small molecules:
long-chain fatty acid anion
2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoserine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8869425