Reaction: PCTP binds PC
- in pathway: Synthesis of PC
Phosphatidylcholine transfer protein (PCTP aka STARD2) is a member of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR)-related lipid transfer (START) domain superfamily, a functionally diverse group of proteins that share a unique structural motif for binding lipids (the START domain). PCTP is widely expressed with highest expression levels in oxidative tissues, including liver, heart, muscle, kidney and brown fat but very little expression in white adipose tissue. PCTP exclusively binds phosphatidylcholine (PC) in the cytosol of cells and may mediate PC exchange at cellular membranes (Roderick et al. 2002). Recent mouse studies reveals a key regulatory role for PCTP in lipid and glucose metabolism. PCTP appears to limit access of fatty acids to mitochondria by binding to (Ersoy et al. 2013) and stimulating the activity of acyl-coenzyme A thioesterase 13 (ACOT13, aka Acyl-CoA thioesterase 13, THEM2), an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of acyl-CoAs to their free fatty acids (Kawano et al. 2014). Ultimately, insulin signaling is downregulated (Kang et al. 2010).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
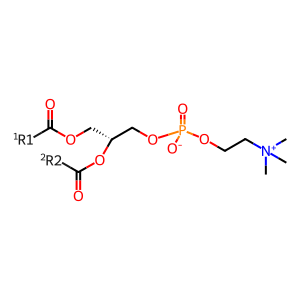
PC [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8873794
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8873794