Reaction: STARD5 binds DCA, LCA
- in pathway: Recycling of bile acids and salts
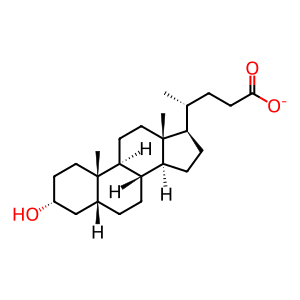
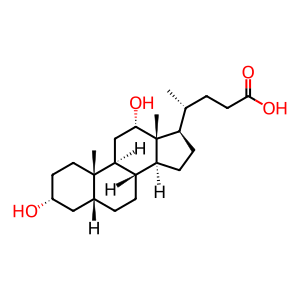
StAR-related lipid transfer protein 5 (STARD5) is highly expressed in at least three cell types targeted by bile acids: liver macrophage Kupffer cells, peripheral macrophages and kidney proximal tubule cells. Unlike the other members of the STARD4 subfamily of the START-containing proteins (members 4 and 6), STARD5 possesses low or no affinity for cholesterol but instead, specifically binds primary and secondary bile acids. STARD5's affinity for the secondary bile acids deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), which lack the alpha-OH in C7, is greater than that of the primary bile acids cholic acid (CA) and chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) (Letourneau et al. 2012, Letourneau et al. 2013). The physiological roles played by STARD5 remain to be elucidated but it could act as a bile acid transporter or sensor.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
LCA [cytosol]
DCA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8873850
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
lithocholate
deoxycholic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8873850