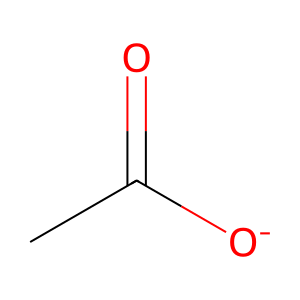
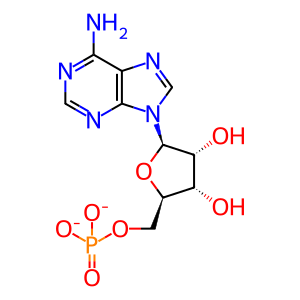
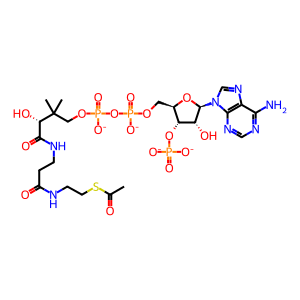
Reaction: ACSS3 ligates CoA to CH3COO-
- in pathway: Synthesis of Ketone Bodies
Mitochondrial acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 3 (ACSS3) belongs to the acyl-coenzyme A synthetase family that catalyse the "activation" of fatty acids by forming a thioester with coenzyme A (CoA-SH). ACSSs typically activate acetate, propionate, or butyrate. Ligation of acetate (CH3COO-) with CoA-SH is described here (Watkins et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AMP [mitochondrial matrix]
PPi [mitochondrial matrix]
Ac-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
CH3COO- [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8875071
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
coenzyme A(4-)
ATP(4-)
acetate
Reaction output - small molecules:
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
diphosphate(3-)
acetyl-CoA(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8875071