Reaction: SLC27A3 ligates CoA-SH to VLCFA
- in pathway: Synthesis of very long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs
Acyl-coenzyme A synthetases catalyse the activation of fatty acids by thioesterification to CoA, the fundamental initial reaction in fatty acid oxidation. Members of the long chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetases (ACSVL) subfamily were originally thought to be fatty acid transport proteins (FATPs), hence their approved gene names and symbols are “solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter) member x" (SLC27Ax) but their transport function has never been proven. Instead, their amino acid sequence contains two highly conserved motifs characteristic of acyl-CoA synthetases. Long-chain fatty acid transport protein 3 (SLC27A3, aka ACSVL3, FATP3) preferentially ligates CoA-SH to very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) (Watkins et al. 2007). The activity of human SLC27A3 is inferred from mouse Slc27a3 functional studies (Pei et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
AMP [mitochondrial matrix]
PPi [mitochondrial matrix]
VLCFA-CoA [mitochondrial matrix]
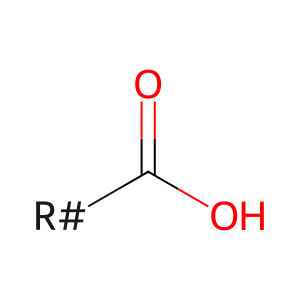
VLCFA [mitochondrial matrix]
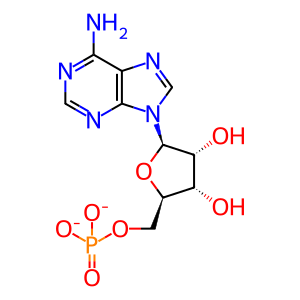
CoA-SH [mitochondrial matrix]
ATP [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8875077
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
very long-chain fatty acid
coenzyme A(4-)
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
diphosphate(3-)
very long-chain fatty acyl-CoA
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8875077