Reaction: NPC2 binds CHOL
- in pathway: LDL clearance
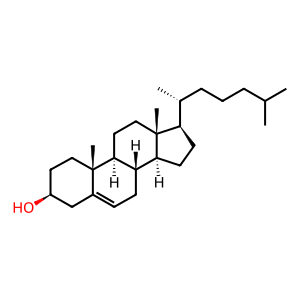
In macrophages, the hydrolysis of cholesteryl esters (CHESTs) is the rate-limiting step in the removal of free cholesterol (CHOL) from these cells. CHOL is transported via transport vesicles and can be used for cellular functions or removed from the cell by ABCA1 to create new HDL particles. Accumulation of CHESTs in macrophage foam cells is key to atherosclerotic plaque formation (Dubland & Francis 2015). Exit from lysosomes of CHOL derived from the hydrolysis of CHESTs in low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) requires the concerted effort of two proteins, membrane-bound Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) and soluble NPC2. In the first step, NPC2 binds unesterified CHOL that has been released from LDLs in the lumen of lysosomes (Liou et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CHOL [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8876472
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8876472