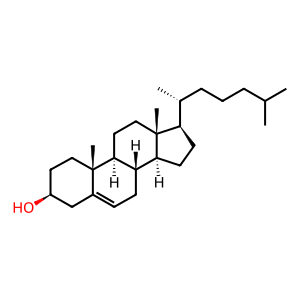
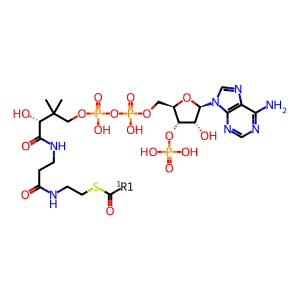
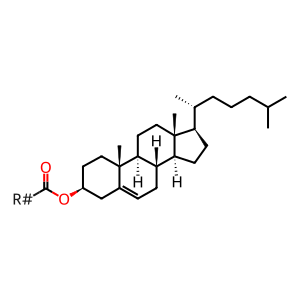
Reaction: SOAT1,2 transfer acyl group to CHOL forming CHEST
- in pathway: LDL clearance
Excess cellular cholesterol (CHOL) is esterified and stored as cholesteryl ester (CHEST). The conversion is catalysed by the ER membrane-residing sterol O-acyltransferases 1 and 2 (SOAT1 and SOAT 2, aka acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1 and 2, ACAT1 and 2) (Chang et al. 1993, Oelkers et al. 1998, Lin et al. 1999). CHESTs are usually present at low levels in most cells but chronic accumulation of CHEST in macrophages causes these cells to appear foamy and is a characteristic of early stage atherosclerosis (Becker et al. 1994). The SOAT enzymes are being investigated as potential drug targets for atherosclerosis and for Alzheimer's disease (Chang et al. 2009). Alzheimer's disease is a prevalent neurodegenerative disease, characterised by a large extracellular accumulation of amyloid plaques, composed mainly of beta-amyloid peptide aggregates. Increases in free cholesterol in the membrane, which can be caused by inhibiting ACAT1, can lead to the decrease of amyloid precursor protein processing. Pharmacological inhibitors of ACAT1 are potential treatment routes for Alzheimer's disease (Puglielli et al. 2001, Chang et al. 2009, Zhu et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CHEST [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
CoA-SH [cytosol]
CHOL [endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
acyl-CoA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8876696
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
cholesterol
acyl-CoA
Reaction output - small molecules:
cholesteryl ester
coenzyme A(4-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8876696