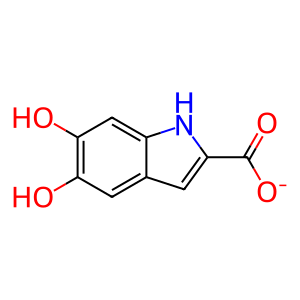
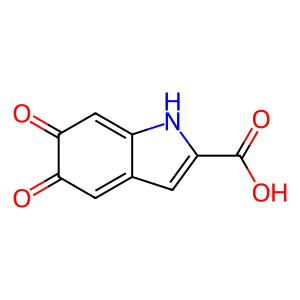
Reaction: TYRP1 oxidises DHICA to IQCA
- in pathway: Melanin biosynthesis
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid oxidase (TYRP1, aka gp75, CAS2, TRP-1) is an abundant protein in the melanosome membrane which, amongst other functions, can oxidise 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) into the corresponding 5,6-indolequinone-2-carboxylic acid (IQCA), thus promoting the incorporation of DHICA units into eumelanin (Olivares et al. 2001). Oculocutaneous albinism (OCA) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by either complete lack of or a reduction of melanin biosynthesis in melanocytes. Mutations in TYRP1 cause OCA3, aka Rufous oculocutaneous albinism. Tyrosinase activity is normal and patients have only a moderate reduction of melanin. Darker-skinned sufferers have bright copper-red colouration of the skin and hair (Kamaraj & Purohit 2014, Rooryck et al. 2006).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
IQCA [melanosome lumen]
H2O [melanosome lumen]
DHICA [melanosome lumen]
O2 [melanosome lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8878581
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylate
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
indole-5,6-quinone-2-carboxylic acid
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8878581