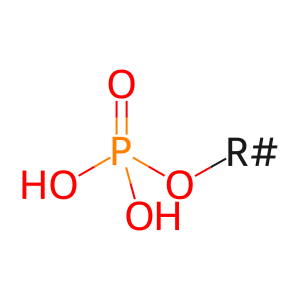
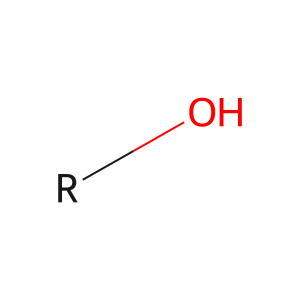
Reaction: ALPI dimer hydrolyses phosphate monoesters
- in pathway: Digestion
Alkaline phosphatases (ALPs) are ubiquitous membrane-bound glycoproteins that catalyse the hydrolysis of phosphate monoesters in alkaline conditions (Sharma et al. 2014). To date, little is known about the physiological function of ALPs in most tissues. In humans, four isozymes exist, named from their tissue localisations. One isozyme, intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI, IAP), possesses alkaline phosphatase activity but has no specific physiological substrate defiend for it yet. It may be involved in the hydrolysis of pro-drugs in the intestine (Lowe et al. 1990).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Alcohol [extracellular region]
Pi [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
phosphate monoester [extracellular region]
Alcohol [extracellular region]
Pi [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
phosphate monoester [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8878787
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
phosphate monoester
water
phosphate monoester
Reaction output - small molecules:
alcohol
hydrogenphosphate
alcohol
hydrogenphosphate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8878787