Reaction: B3GALNT1 transfer GalNAc to Gb3Cer to form Gb4Cer
- in pathway: Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis
Globosides are a type of glycosphingolipid with more than one sugar as the side chain of ceramide, usually a combination of N-acetylgalactosamine, D-glucose or D-galactose. They are components of cellular membranes, especially of the kidneys, red blood cells, blood serum, liver and spleen. Globoside synthesis (and therefore accummulation) increases in pathological conditions including neurodegenerative disorders, immune diseases and cancer. UDP-GalNAc:beta-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 (B3GALNT1, B3GALT3) is a Golgi membrane-associated protein that can add N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to globotriaosylceramide (Gb3Cer) to form Gb4Cer (Okajima et al. 2000, Amado et al. 1998).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
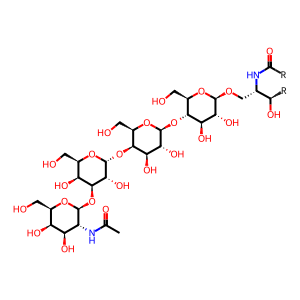
Gb4Cer [Golgi membrane]
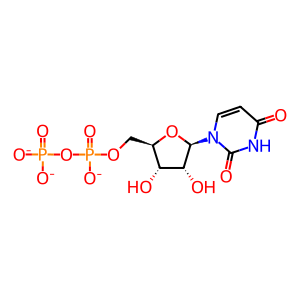
UDP [Golgi lumen]
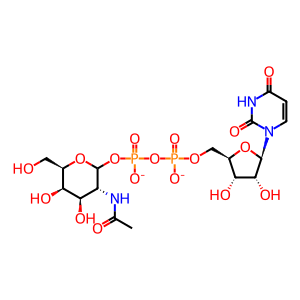
UDP-GalNAc [Golgi lumen]
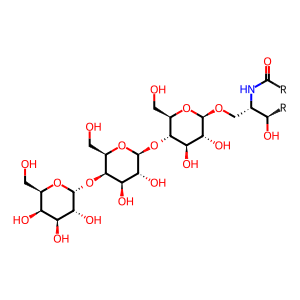
Gb3Cer [Golgi membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8878914
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine(2-)
alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1)-ceramide
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-galactosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucosyl-(1<->1')-ceramide
UDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8878914