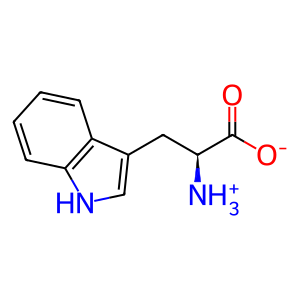
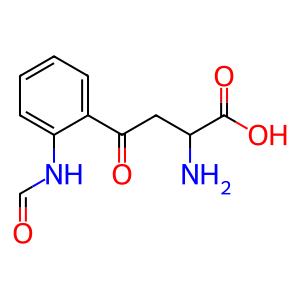
Reaction: IDO2 dioxygenates L-Trp to NFK
- in pathway: Tryptophan catabolism
Cytosolic indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 2 (IDO2) catalyzes the conversion of L-tryptophan and oxygen to formylkynurenine. The catalytic properties of the human enzyme have been analyzed directly; the subcellular location and monomeric state of the active form of the enzyme are inferred from the properties of its rabbit ortholog. In the body, IDO2 mRNA can be detected in a variety of cells, including dendritic cells, consistent with a normal role in immune function and a pathological one in tumor progression. Two IDO2 variants common in human populations encode enzymatically inactive protiens, suggesting that absence of IDO2 activity may be common in humans (Metz et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
NFK [cytosol]
L-Trp [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-888614
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
L-tryptophan zwitterion
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
N-formylkynurenine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-888614