Reaction: CD38 hydrolyses NAD+ to NAM and ADP-ribose
- in pathway: Nicotinate metabolism
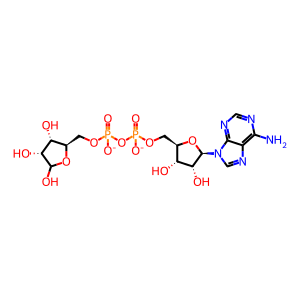
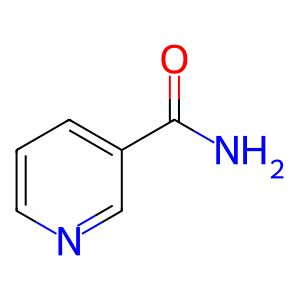
ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase 1 (CD38) is a multifunctional enzyme that can catalyse the hydrolysis of NAD+ to form linear ADP-ribose (ADP-D-ribose) and/or cyclization of NAD+ forming cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) via a two-step enzymatic reaction. The first common step involves the cleavage of the nicotinamide group of NAD+. The reaction intermediate can either be hydrolysed to form ADP-D-ribose or cyclized to form cADPR (Lee et al. 1995, Moreschi et al. 2006). CD38 can also produce nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) (Lee et al. 1999). Both cADPR and NAADP are established second messengers for mobilising intracellular Ca2+ stores (Lee 2012). The reaction annotated here describes the hydrolysis of NAD+ to form ADP-D-ribose.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [extracellular region]
ADP-ribose [extracellular region]
NAM [extracellular region]
NAD+ [extracellular region]
H2O [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8938076
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NAD(1-)
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
ADP-D-ribose(2-)
nicotinamide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8938076