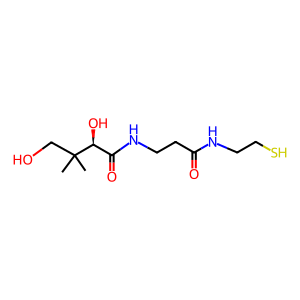
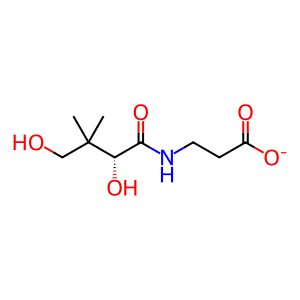
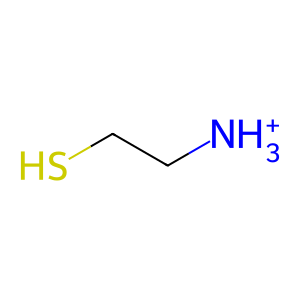
Reaction: Vanin hydrolyses pantetheine to PanK, 2AET
- in pathway: Vitamin B5 (pantothenate) metabolism
Vanin (VNN1) is a membrane pantetheine hydrolase or pantetheinase (EC 3.56.1.-) (Maras et al. 1999, Martin et al. 2001), part of a cluster of three human orthologous genes (VNN1, VNN2, VNN3) on Chr. 6q22-24 (Kaskow et al. 2012, Boersma et al. 2014). VNN3 is a pseudogene in humans. Vanins catalyse the hydrolysis of pantetheine to pantothenic acid (PanK, vitamin B5) and cysteamine (2AET), a powerful anti-oxidant. PanK is the initial substrate for the synthesis of Coenzyme A (CoA-SH).
Mouse Vnn1 has been shown to be GPI-anchored to the outer face of the plasma membrane. Sequence motifs conserved with human VNN1 and VNN2 supports the inference that the human proteins are similarly anchored (Aurand-Lions et al. 1996; Naquet et al. 2020), so the enzymes are annotated as acting on extracellular panthetheine to generate extracellular PanK and 2AET.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PanK [extracellular region]
2AET [extracellular region]
Pantetheine [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8938300
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
pantetheine
Reaction output - small molecules:
(R)-pantothenate
cysteaminium
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8938300