Reaction: UGT1A10 transfers GlcA from UDP-GlcA to GCTN
- in pathway: Glucuronidation
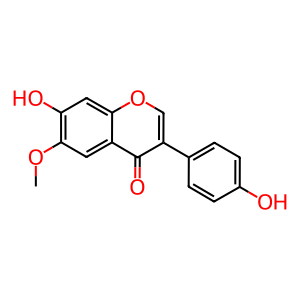
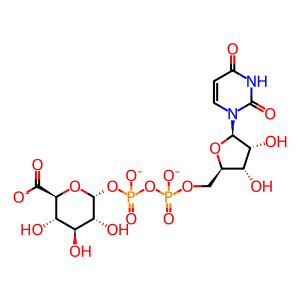
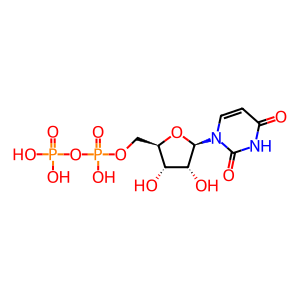
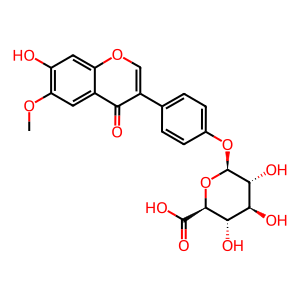
Isoflavones are a class of dietary polyphenols called phytoestrogens which are found in soy and soy foods, alfalfa sprouts and red clover. They possess biological activities ranging from anticancer to cardiovascular protective effects (Zhou et al. 2016). Despite their health claims, making these compounds into chemo-preventive or chemo-therapeutic agents is complicated by their low bioavailabilities (<5%), the result of extensive first-pass metabolism by phase II enzymes including UGTs and SULTs (Hu 2007). Four UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A (UGT1A) isoforms share the responsibility of metabolising various isoflavones. UGT1A10 is mainly expressed in the intestine and is located on the ER membrane of these cells. It can transfer the glucuronyl moiety from UDP-GlcA to the isoflavone glycitein (GCTN) to form glycitein 4-O-glucuronide (GCTN4OG) (Tang et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UDP [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
GCTN4OG [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
GCTN [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
UDP-GlcA [endoplasmic reticulum lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8941701
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glycitein
UDP-alpha-D-glucuronate(3-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP
glycitein 4'-O-glucuronide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8941701