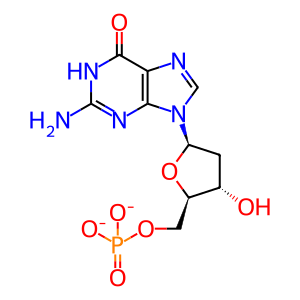
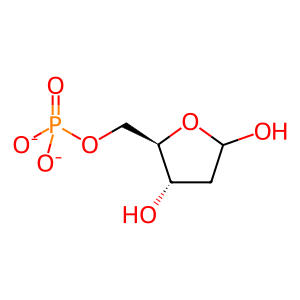
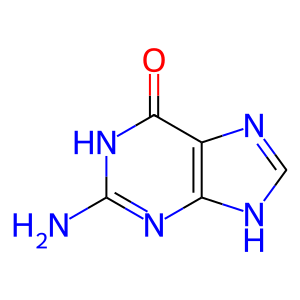
Reaction: DNPH1 hydrolyses dGMP
- in pathway: Purine catabolism
2'-deoxynucleoside 5'-phosphate N-hydrolase 1 (DNPH1 aka c-Myc-responsive protein RCL) is a cytosolic protein which catalyses the cleavage of the N-glycosidic bond of deoxyribonucleoside 5'-monophosphates to yield deoxyribose 5-phosphate (2DORP) and a purine or pyrimidine base. Of the six 2'-deoxynucleoside 5'-monophosphates, DNPH1 has highest affinity for the purine deoxynucleotide dGMP (Amiable et al. 2013). The same affinity for purine deoxynucleotides over pyrimidine deoxynucleotides was observed for rat Dnph1 (Ghiorghi et al. 2007). DNPH1 is a potential target for anti-cancer therapies (Amiable et al. 2014) as it is involved in cellular proliferation and is up-regulated in several types of cancer.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
2DORP [cytosol]
Gua [cytosol]
dGMP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8953339
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
2'-deoxyguanosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
2-deoxy-D-ribofuranose 5-phosphate(2-)
guanine
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8953339