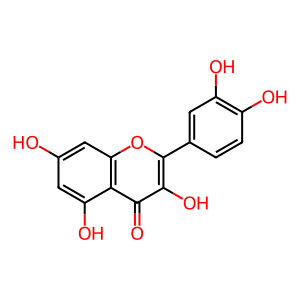
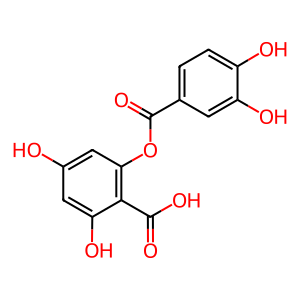
Reaction: PIR oxygenates quercetin
- in pathway: Digestion
Quercetin is an abundant flavonoid found in edible vegetables, grains and fruits and is used as an ingredient in supplements, beverages, or foods. Pirin (PIR) is a highly conserved nuclear protein (Wendler et al. 1997) which possesses quercetinase activity, transforming quercetin to 2-protocatechuoylphloroglucinol carboxylic acid (2PCPGCA) and carbon monoxide (CO) (Adams & Jia 2005). Quercetin supplements have been promoted for the treatment of a wide spectrum of diseases including cancer but there is insufficient evidence to draw any conclusive proof of its beneficial effects to date (Miles et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
CO [nucleoplasm]
2PCPGCA [nucleoplasm]
quercetin [nucleoplasm]
O2 [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8953398
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
quercetin
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
carbon monoxide
2-(3,4-dihydroxybenzoyloxy)-4,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8953398