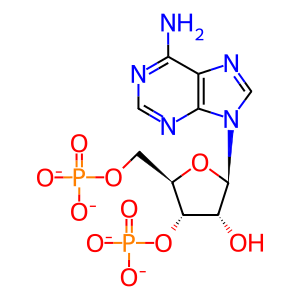
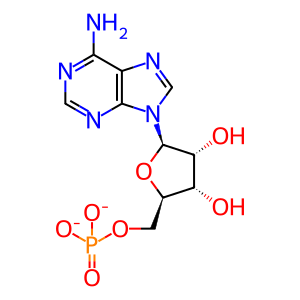
Reaction: IMPAD1 hydrolyses PAP to AMP
- in pathway: Cytosolic sulfonation of small molecules
Sulfur is an essential element in all lifeforms used in the synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids, maintenance of cellular redox states and detoxifying toxic compounds. 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is the active form of sulfur used in these reactions, which consume PAPS, producing 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphate (PAP). PAP is degraded to 5′-AMP (AMP) by 3′-nucleotidase family. Mammals encode two 3′-nucleotidases, the Golgi-resident inositol monophosphatase 3 (IMPAD3 aka PAP phosphatase, gPAPP) and the cytosolic bisphosphate 3′-nucleotidase 1 (BPNT1, described in its own reaction). Both require Mg2+ as cofactor and both are inhibited by lithium (Hudson et al. 2013).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [Golgi lumen]
adenosine 5'-monophosphate [Golgi lumen]
PAP [Golgi lumen]
H2O [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8953499
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
adenosine 3',5'-bismonophosphate(4-)
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8953499