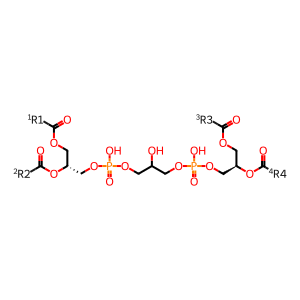
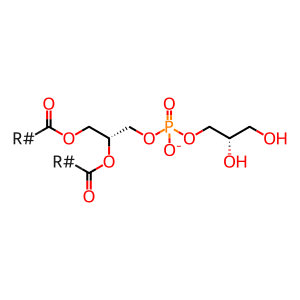
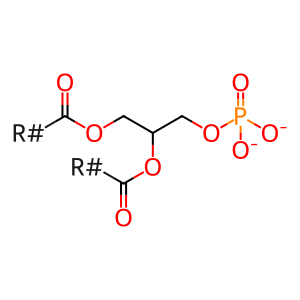
Reaction: PLD6 dimer hydrolyses cardiolipin to PA and PG
- in pathway: Synthesis of PA
Mitochondrial cardiolipin hydrolase (PLD6 aka MitoPLD) is located on the outer mitochondrial membrane and promotes trans-mitochondrial membrane adherence (mitochondrial fusion) in a Mfn-dependent manner by hydrolysing cardiolipin to generate the acidic fusogenic lipid phosphatidic acid (PA) and phosphatidylglycerol (PG) (Choi et al. 2006). Although cardiolipin is primarily an inner mitochondrial membrane-located protein, the outer mitochondrial membrane also contains around 10-20% cardiolipin and cardiolipin has been shown to translocate in a regulatable manner between the compartments (Liu et al. 2003). Mitoguardin 1 and 2 (MIGA1 and MIGA2) are regulators of mitochondrial membrane fusion. They form homo- or hetero-dimers at the mitochondrial outer membrane where they interact with PLD6 to stabilise it and/or facilitate PLD6 dimer formation (Zhang et al. 2016).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
PG [mitochondrial outer membrane]
PA [mitochondrial outer membrane]
H2O [mitochondrial intermembrane space]
cardiolipin [mitochondrial outer membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8954398
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
cardiolipin
Reaction output - small molecules:
1,2-diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-sn-glycerol)(1-)
phosphatidate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8954398