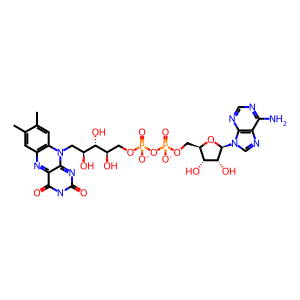
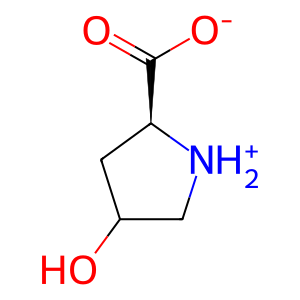
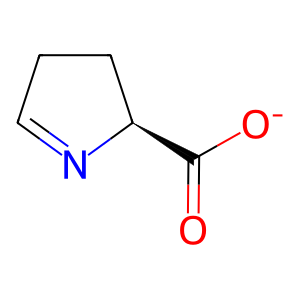
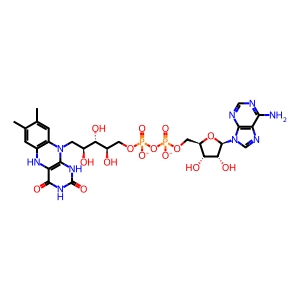
Reaction: PRODH2 oxidises HPRO to 1PYR-5COOH
- in pathway: Proline catabolism
The catabolism of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline (HPRO) and proline (L-Pro) (from endogenous and dietary sources of collagen) makes a significant contribution to the glyoxylate pool in humans. The dehydrogenation (oxidation) of HPRO/L-Pro to L-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (1PYR-5COOH) coupled to the conversion of FAD to FADH2 is the first step in proline catabolism. Proline dehydrogenases (PRODHs), located at the inner mitochondrial membrane mediate this reaction. Whereas PRODH prefers L-Pro as substrate, PRODH2 has a clear preference for HPRO (Summitt et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
1PYR-5COOH [mitochondrial matrix]
FADH2 [mitochondrial inner membrane]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
FAD [mitochondrial inner membrane]
HPRO [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8955817
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
FAD(3-)
4-hydroxy-L-proline zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
(S)-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate
FADH2(2-)
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8955817