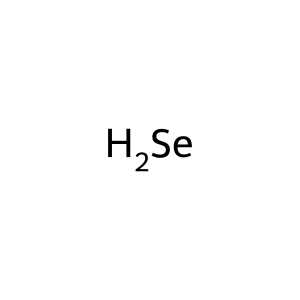
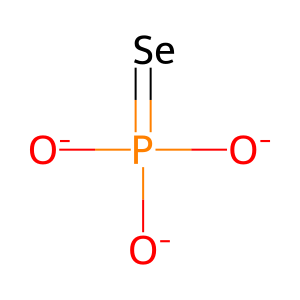
Reaction: SEPHS2 phosphorylates H2Se to form SELP
- in pathway: Selenocysteine synthesis
Selenoproteins are proteins that incorporate the nonstandard amino acid selenocysteine (Sec) in response to the UGA codon. Sec is synthesised in several steps from hydrogen selenide (H2Se), an intermediate formed from dietary sources of selenium. In the first step, cytosolic selenide water dikinase 2 (SEPHS2 aka SPS2) mediates the phosphorylation of H2Se using ATP as the phosphate donor, forming selenophosphate (SELP) (Tamura et al. 2004).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
H+ [cytosol]
SELP [cytosol]
AMP [cytosol]
H2Se [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-8959510
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
selane
water
ATP(4-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
hydron
selenophosphate
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-8959510