Reaction: PDE12 cleaves 2'-5' oligoadenylates
- in pathway: OAS antiviral response
Viral infection produces dsRNA that activates OAS isozymes to synthesize 5'-triphosphorylated 2'-5'-linked oligoadenylate (2-5A). Latent ribonuclease L (RNase L) binds 2-5A and oligomerizes into an active complex capable of cleaving ssRNA into retinoic acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine rich repeat and pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome-activating small RNAs (Malathi K et al. 2007; Chakrabarti A et al. 2015). Activation of RNase L can be attenuated by 2′-phosphodiesterase (PDE12)- mediated degradation of 2-5A. PDE12 is an endonuclease/exonuclease/phosphatase family member of deadenylases with both 3’,5’- and 2’,5’-phosphodiesterase activities. PDE12 localizes to the mitochondrial matrix and, in addition to degrading 2-5A, removes poly(A) tails from some mitochondrial mRNAs (Kubota K et al. 2004; Poulsen JB et al. 2011; Rorbach J et al. 2011; Silverman RH & Weiss SR 2014; Wood ER et al. 2015). The 2H phosphoesterase, AKAP7, is an unrelated nuclear enzyme that also degrades 2-5A (Gusho E et al. 2014). Several viruses, including some coronaviruses and rotaviruses, encode structurally related 2H phosphoesterases (each with two conserved histidine motifs) that degrade 2-5A and antagonize RNase L mediated antiviral activity (Zhao L et al. 2012; Zhang R et al. 2013; Silverman RH & Weiss SR 2014; Ogden KM et al. 2015; Sui B et al. 2016; Thornbrough JM et al. 2016; Goldstein SA et al. 2017).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
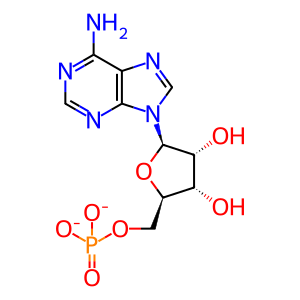
AMP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9009950
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
ATP(4-)
adenosine 5'-monophosphate(2-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9009950