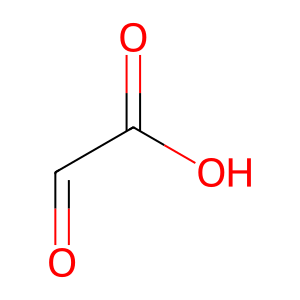
Reaction: GSTZ1 dimer dehalogenates DCA to glyoxylate
- in pathway: Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) complex
In the liver, dimeric glutathione S-transferase zeta 1 (GSTZ1 dimer, aka maleylacetoacetate isomerase, MAAI) mediates the dechlorination of the drug dichloroacetate (DCA) to glyoxylate (Ammini & Stacpoole 2003, Stacpoole et al. 1998, 2008). GSTZ1 is primarily found both in the cytosol and mitochondria (Li et al. 2011). Glyoxylate, the primary metabolite of DCA metabolism, is ultimately converted to oxalate and glycine. The reaction requires (but does not consume) glutathione (GSH). GSTZ1 also catalyses the penultimate step in tyrosine catabolism, thus avoiding the accumulation of toxic tyrosine intermediates. DCA inhibits its own metabolism apparently by a post-translationally mediated inhibition of hepatic GSTZ1 (Stacpoole et al. 1998). GSTZ1 inhibition can cause the build-up of tyrosine intermediates which are able to form protein adducts. Chronic administration of DCA in adult rodents, dogs and some humans causes reversible peripheral neuropathy and hepatotoxicity, possibly because of these reactive tyrosine intermediates (Stacpoole et al. 1998, James et al. 2017). The rate of GSTZ1 inactivation by DCA is influenced by age, GSTZ1 haplotype and cellular chloride concentration (Shroads et al. 2008, 2012, 2015, Jahn et al. 2016, James et al. 2017).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
glyoxylate [mitochondrial matrix]
HCl [mitochondrial matrix]
H2O [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9011595
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
Reaction output - small molecules:
glyoxylic acid
hydrogen chloride
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9011595