Reaction: ME3:Mg2+ tetramer oxidatively decarboxylates MAL to PYR
- in pathway: Citric acid cycle (TCA cycle)
One hallmark of cancer is altered cellular metabolism. Malic enzymes (MEs) are a family of homotetrameric enzymes that catalyse the reversible oxidative decarboxylation of L-malate to pyruvate, with a simultaneous reduction of NAD(P)+ to NAD(P)H. As MEs generate NADPH and NADH, they may play roles in energy production and reductive biosynthesis. Humans possess three ME isoforms; ME1 is cytosolic and utilises NADP+, ME3 is mitochondrial and can utilise NADP+ and ME2 is mitochondrial and can utililse either NAD+ or NADP+ (Chang & Tong 2003, Murugan & Hung 2012).
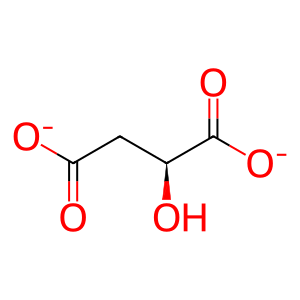
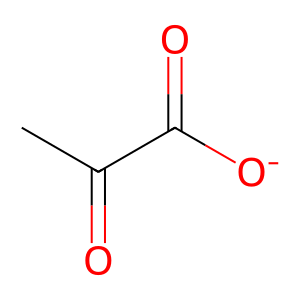
NADP-dependent malic enzyme (ME3, aka m-NADP-ME) is a mitochondrial enzyme that oxidatively decarboxylates (s)-malate (MAL) to pyruvate (PYR) and CO2 using NADP+ as cofactor (Loeber et al. 1994). ME1 exists as a dimer of dimers (Murugan & Hung 2012) and a divalent metal such as Mg2+ is essential for catalysis (Chang & Tong 2003). ME3 may play a role in insulin secretion (Hasan et al. 2015) but how it does this in panceratic beta cells has not been established yet.
NADP-dependent malic enzyme (ME3, aka m-NADP-ME) is a mitochondrial enzyme that oxidatively decarboxylates (s)-malate (MAL) to pyruvate (PYR) and CO2 using NADP+ as cofactor (Loeber et al. 1994). ME1 exists as a dimer of dimers (Murugan & Hung 2012) and a divalent metal such as Mg2+ is essential for catalysis (Chang & Tong 2003). ME3 may play a role in insulin secretion (Hasan et al. 2015) but how it does this in panceratic beta cells has not been established yet.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H+ [mitochondrial matrix]
PYR [mitochondrial matrix]
NADPH [mitochondrial matrix]
CO2 [mitochondrial matrix]
NADP+ [mitochondrial matrix]
MAL [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9012349
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
NADP(+)
(S)-malate(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydron
pyruvate
NADPH
carbon dioxide
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9012349