Reaction: Ac-PTGS2 dimer oxidises DHA to 17(R)-Hp-DHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DHA-derived SPMs
Normally, cyclooxygenases (COX) carry out stereospecific oxygenation of arachidonic acid to generate prostaglandins. When treated with aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid, ASA), dimeric cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2, PTGS2 dimer) can be acetylated. ASA covalently modifies PTGS2 by acetylating a serine residue at position 530 within the cyclooxygenase active site (Lucido et al. 2016). Acetylated PTGS2 dimer (Ac-PTGS2 dimer) changes the oxygenation stereospecificity towards its substrates, perhaps by steric shielding effects (Tosco 2013), producing a shift in lipid mediator production. Ac-PTGS2 dimer is able to incorporate molecular oxygen into ω-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), present in inflammatory exudates, to form the 17(R) epimer 17(R)-hydroperoxy-docosahexaenoic acid (17(R)-Hp-DHA) (Serhan et al. 2002, Sun et al. 2007). The product can either be transformed into aspirin-triggered D-resolvins or aspirin-triggered protectin D1 (Serhan et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
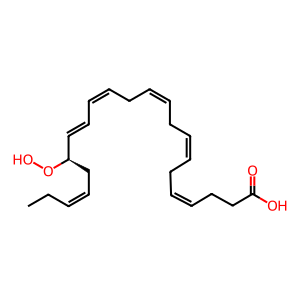
17(R)-Hp-DHA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
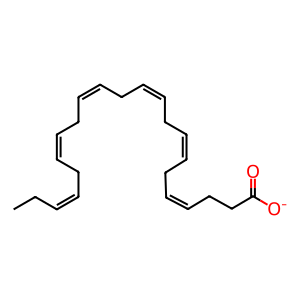
DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9020261
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate
Reaction output - small molecules:
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,15E,17R,19Z)-17-hydroperoxydocosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9020261