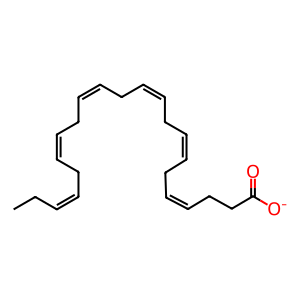
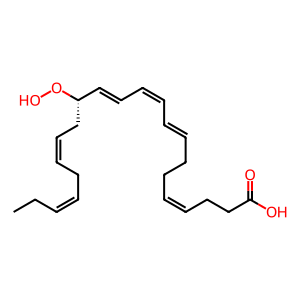
Reaction: ALOX12:Fe2+ oxidises DHA to 14(S)-Hp-DHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DHA-derived SPMs
Maresins are a family of anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving lipid mediators biosynthesized from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by macrophages. In the first step, DHA is oxygenated by lipoxygenase 12 using Fe2+ cofactor (ALOX12:Fe2+) to 14(S)-hydroperoxy-docosahexaenoic acid (14(S)-Hp-DHA) (Serhan et al. 2009, Deng et al. 2014). Maresin-like mediators MaR-L1 and Mar-L2 are produced by leukocytes and platelets and have been shown to restore reparative functions of diabetic macrophages in wounds (Brem & Tomic-Canic 2007, Hong et al. 2014). The same reaction as above can occur in human leukocytes and platelets to produce MaR-L1 and MaR-L2. The 14(S)-Hp-DHA intermediate can also serve as a precursor for maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration (MCTR) (Dalli et al. 2016).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
14(S)-Hp-DHA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9020274
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate
Reaction output - small molecules:
(4Z,8E,10Z,12E,14S,16Z,19Z)-14-hydroperoxydocosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9020274