Reaction: Epoxide hydrolase hydrolyses 13,14-epoxy-DPAn-3 to MaR1n-3 DPA or MaR2n-3 DPA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DPAn-3-derived maresins
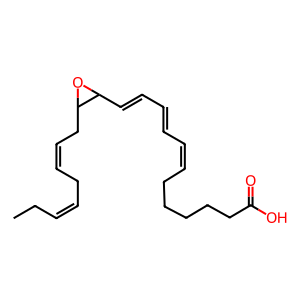
In a reaction scheme similar to the one for DHA-derived maresins, 13,14(S)-epoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (13,14(S)-epoxy-DPAn-3) can be hydrolysed by an epoxide hydrolase to form either 7(R),14(S)-dihydroxy-docosapentaenoic acid (MaR1n-3 DPA) or 13,14(S)-dihydroxy-docosapentaenoic acid (MaR2n-3 DPA) (Dalli et al. 2013). MaR1n-3 DPA and MaR2n-3 DPA are named after maresin-1 (derived from DHA) as they share an alcohol group at C14 and are proposed to possess similar anti-inflammatory and proresolving potency and activity as maresin-1. With human leukocytes these n-3 DPA-SPMs reduced neutrophil chemotaxis, adhesion and enhanced macrophage phagocytosis (Dalli et al. 2013, Vik et al. 2017). The total chemical synthesis of MaR1n-3 DPA had been reported for the first time in 2014 (Tungen et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [cytosol]
13,14(S)-epoxy-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9025998
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
(7Z,9E,11E,16Z,19Z)-13,14-epoxydocosapentaenoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9025998