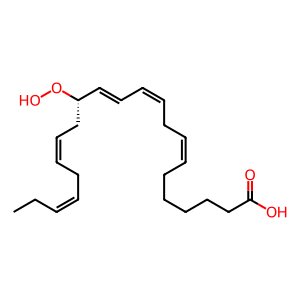
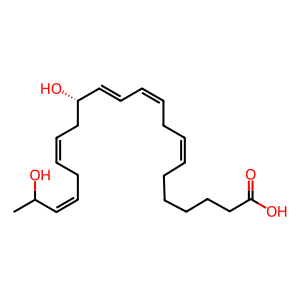
Reaction: ALOX5 oxidises 14(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 to MaR3n-3 DPA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of DPAn-3-derived maresins
In an alternative reaction to epoxidation, 14(S)-hydroperoxy-docosapentaenoic acid (14(S)-HpDPAn-3) can undergo a second oxygenation at the ω-1 position to yield 14(S), 21-dihydroxy-docosapentaenoic acid (MaR3n-3 DPA) (Dalli et al. 2013). MaR3n-3 DPA is named after maresin-1 (derived from DHA) as they share an alcohol group at C14 and is proposed to possess similar anti-inflammatory and proresolving potency and activity as maresin-1. With human leukocytes this n-3 DPA-SPM reduced neutrophil chemotaxis, adhesion and enhanced macrophage phagocytosis (Dalli et al. 2013, Vik et al. 2017). If, as assumed, DPA metabolism follows the same path as DHA metabolism, the lipoxygenase could be the dual-functional 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
MaR3n-3 DPA [cytosol]
14(S)-Hp-DPAn-3 [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9026005
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(7Z,10Z,12E,14S,16Z,19Z)-14-hydroperoxydocosapentaenoic acid
dioxygen
Reaction output - small molecules:
14(S),21-dihydroxy-(7Z,10Z,12E,16Z,19Z)-docosapentaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9026005