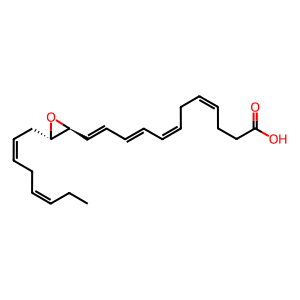
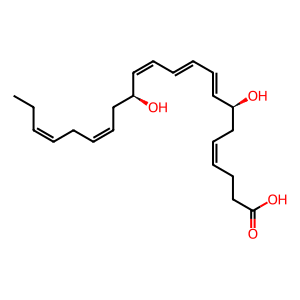
Reaction: Non-enzymatic hydrolysis hydrolyses 13(S),14(S)-epoxy-DHA to 7-epi-MaR1
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of maresins
Maresin 1 (MaR1, 7(R),14(S)-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid) is the first identified maresin and displays potent anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving actions (Serhan et al. 2012, Chatterjee et al. 2014). MaR1 was found to inhibit proinflammatory mediator production by inhibiting LTA4 hydrolase, thereby shifting macrophage phenotype from proinflammatory mediator to proresolving mediator production (Dalli et al. 2013). A novel double dioxygenation product can also be formed by non-enzymatic hydrolysis of 13(R),154(S)-epoxy-DHA, namely 7(S),14(S)-dihydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (7-epi-MaR1). Although 7-epi-MaR1 possesses some bioactivity, it displays lower anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving actions than MaR1 (Serhan et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
7-epi-MaR1 [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
13(S),14(S)-epoxy-DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9026544
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
(13S,14S)-epoxy-(4Z,7Z,9E,11E,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
(7S,14S)-dihydroxy-(4Z,8E,10E,12Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9026544