Reaction: GGT transfers GSH to 16S,17S-epoxy-DHA to form PCTR1
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of protectin and resolvin conjugates in tissue regeneration (PCTR and RCTR)
Human macrophages produce protectin conjugates in tissue regeneration (PCTR). PCTR are named as such because they share a proposed biosynthetic pathway, structural features, and biological actions with DHA-derived protectins as well as displaying potent tissue-regenerative actions. 16S,17S-epoxy-docosahexaenoic acid (16S,17S-epoxy-DHA) was found to be a substrate for a glutathione transferase (GGT) which produces PCTR1 (16-glutathionyl, 17-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid) in greater quantities in M2-type macrophages than M1-type macrophages and was found to enhance resolution of infectious inflammation (Ramon et al. 2016, Dalli et al. 2015).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
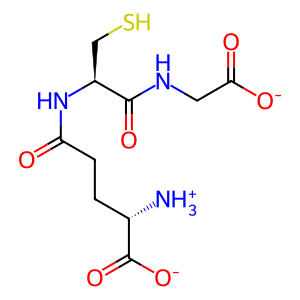
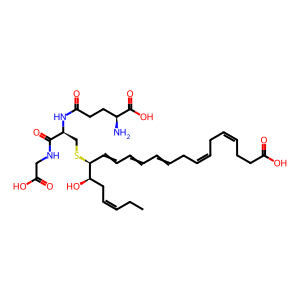
PCTR1 [cytosol]
GSH [cytosol]
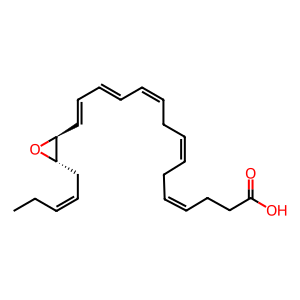
16S,17S-epoxy-DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9026901
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glutathionate(1-)
(16S,17S)-epoxy-(4Z,7Z,10Z,12E,14E,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
16(S)-glutathionyl-17(R)-hydroxy-(4Z,7Z,10,12,14,19Z)-docosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9026901