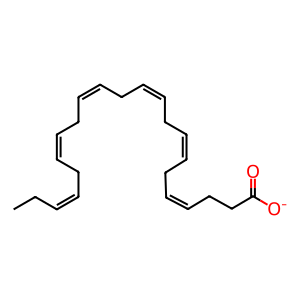
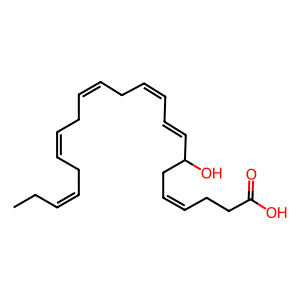
Reaction: ALOX5 oxidises DHA to 7-HDHA
- in pathway: Biosynthesis of electrophilic ω-3 PUFA oxo-derivatives
In human neutrophils, 5-lipoxygenase (ALOX5) can mediate the lipoxygenation of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) to 7-hydroxy-docosahexaenoic acid (7-HDHA) (Cipollina et al. 2014). Neutrophils treated with an ALOX5 inhibitor completely suppressed the formation of 7-oxo-DHA and its hydroxy precursor 7-HDHA, demonstrating that ALOX5 mediates the first step in 5-oxo-DHA biosynthesis (Cipollina et al. 2014).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
7-HDHA [cytosol]
O2 [cytosol]
DHA [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9027624
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dioxygen
(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-docosahexaenoate
Reaction output - small molecules:
(4Z,8E,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-7-hydroxydocosahexaenoic acid
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9027624