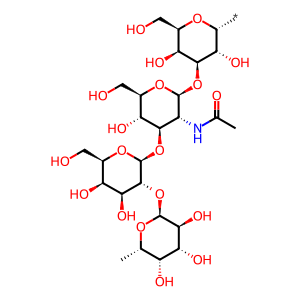
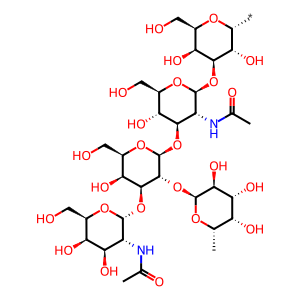
Reaction: sABO-A:Mn2+ transfers GalNAc to H antigen-sec to form A antigen-sec
- in pathway: ABO blood group biosynthesis
As well as being a Golgi membrane resident, the histo-blood group ABO system transferase (ABO) can be proteolytically processed by an unknown protease into a soluble form, fucosylglycoprotein alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase (sABO). A, B and AB individuals express glycosyltransferase activities that convert the H antigen to the A antigen (by addition of GalNAc), to the B antigen (by addition of Gal) or to the AB antigen (by the addition of both GalNAc and Gal). O group individuals lack such activity. Differences in four critical amino acids (176, 235, 266 and 268) alter the specificity from an A to a B glycosyltransferase (Yamamoto et al. 1990, Yamamoto & McNeill 1996, Seto et al. 1999, Alfaro et al. 2008). The soluble form of histo-blood group A transferase (sABO-A) utilises UDP-GalNAc to transfer N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to the H antigen formed via Type 1 chains to form the A antigen in secretors (A antigen-sec) (Patenaude et al. 2002, Persson et al. 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
UDP [extracellular region]
A antigen-sec [extracellular region]
H antigen-sec [extracellular region]
UDP-GalNAc [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9034042
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
alpha-L-Fuc-(1->2)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Gal-yl group
UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP(3-)
alpha-L-Fuc-(1->2)-[alpha-D-GalNAc-(1->3)]-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Gal-yl group
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9034042