Reaction: Defective MPDU1 does not promote transfer of Man to (GlcNAc)2 (Man)8 (PP-Dol)1 by ALG9
- in pathway: Defective MPDU1 causes CDG-1f
Mannose-P-dolichol utilisation defect 1 protein (MPDU1) is required for the efficient utilisation of the mannose donor dolichyl-phospho-mannose (DOLPman) in the synthesis of both lipid-linked oligosaccharides (LLOs) and glycosylphosphatidylinositols by mannosyltransferases ALG3, ALG9 and ALG12. Defects in MPDU1 can cause congenital disorder of glycosylation 1f (MPDU1-CDG, CDG-1f; MIM:609180), a multisystem disorder caused by a defect in glycoprotein biosynthesis and characterised by under-glycosylated serum glycoproteins of varying sizes. CDG type 1 diseases result in a wide phenotypic spectrum, such as poor neurological development, psychomotor retardation, dysmorphic features, hypotonia, coagulation abnormalities and immunodeficiency. In this condition, DOLPman is no longer utilised in transferase reactions extending LLOs, even as substrate levels and transferase enzyme activities appear normal (Anand et al. 2001, Schenk et al. 2001). Point mutations that can cause MPDU1-CDG are G73E, L119P, M1T, L74S as well as the frameshift mutation L171Sfs*42 (Schenk et al. 2001, Kranz et al. 2001).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
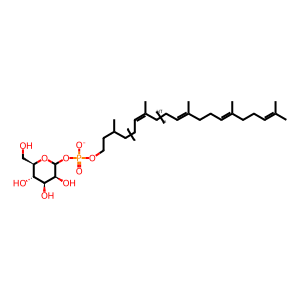
DOLP-Man [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
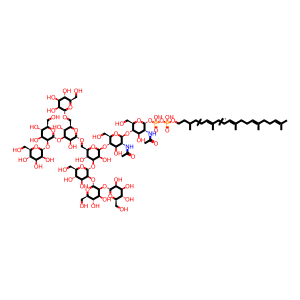
(GlcNAc)2 (Man)8 (PP-Dol)1 [integral component of lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9036020
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
dolichyl D-mannosyl phosphate(1-)
alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-Man-(1->6)-[alpha-Man-(1->2)-alpha-Man-(1->3)]-alpha-Man-(1->6)]-beta-Man-(1->4)-beta-GlcNAc-(1->4)-alpha-GlcNAc(PP-Dol)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9036020