Reaction: Defective IDUA does not hydrolyse the unsulfated alpha-L-iduronosidic link in DS
- in pathway: MPS I - Hurler syndrome
Absence of alpha-L-iduronidase (IDUA, MIM:252800), the enzyme responsible for the removal of non-reducing terminal alpha-L-iduronide (Lido) residues during the lysosomal degradation of heparan sulphate (HS) and dermatan sulfate (DS) is the cause of MPS I disorders (MIM:607014). The nonsense mutations, W402X and Q70X and the rarer P553R account for approximately 50% of all MPS I alleles in patients with predominantly European origins (Scott et al. 1992, Bunge et al. 1994, Scott et al. 1992b). There are, however, considerable differences in the frequency of these mutations in patients from Norway and Finland when compared with other Eurpoean countries. In Scandinavia, W402X and Q70X account for 17% and 62% of the MPSI alleles, respectively, while in the other European countries W402X is about 2.5 times more frequent (48%) than Q70X (19%).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [lysosomal lumen]
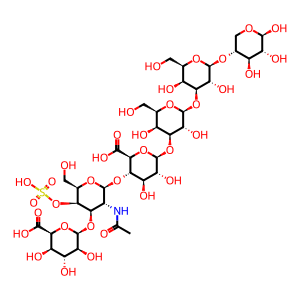
IdoA-GalNAc(4S)-GlcA-Gal-Gal-Xyl [lysosomal lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9036041
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
beta-D-IdopA-(1->3)-beta-D-GalpNAc4S-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcpA-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-beta-D-Xylp
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9036041