Reaction: FUT2 transfers Fuc to Type 1 chains to form H antigen-sec
- in pathway: ABO blood group biosynthesis
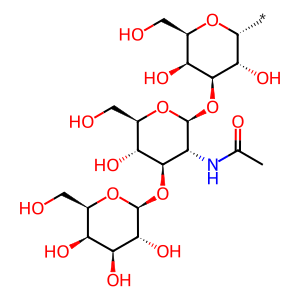
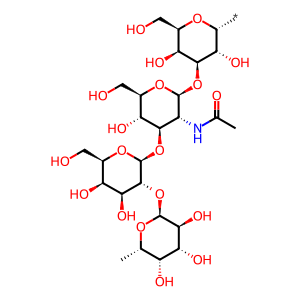
The H antigen is formed by the addition of a fucose (Fuc) sugar onto one of two precursor oligosaccharide sequences; Type 1 or Type 2 chains. Type 2 chains are found on red blood cells (RBCs), epithelial cells and endothelial cells whereas Type 1 chains are primarily found in bodily secretions. The FUT2 gene (aka Se gene) is expressed in secretory epithelial cells in salivary glands and the gastrointestinal tract and produces galactoside 2-α-L-fucosyltransferase 2 (FUT2 aka α-1,2-fucosyltransferase 2) which mediates the transfer of a Fuc sugar to the galactose (Gal) sugar of the Type 1 chain precursor Gal-β1,3-GlcNAc-β1,3-Gal-R (where R is a glycoprotein) to form the H antigen (Kelly et al. 1995, Koda et al. 1997). This is an essential step for subsequent formation of A and B antigens. Mutations that inactivate the FUT2 gene can result in the 'Bombay phenotype' where no A, B or H antigens are produced in secretions (Koda et al 1997b, Kelly et al. 1994).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
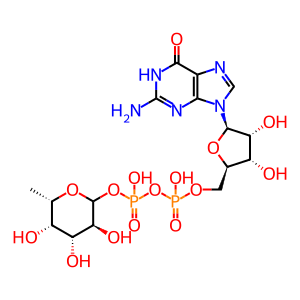
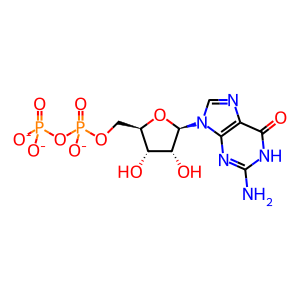
GDP [Golgi lumen]
H antigen-sec [Golgi lumen]
Type 1 chain [Golgi lumen]
GDP-Fuc [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9036987
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Gal-yl group
GDP-L-fucose
Reaction output - small molecules:
GDP(3-)
alpha-L-Fuc-(1->2)-beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Gal-yl group
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9036987