Reaction: 27-hydroxysterol binds ESR1, ESR2
- in pathway: ESR-mediated signaling
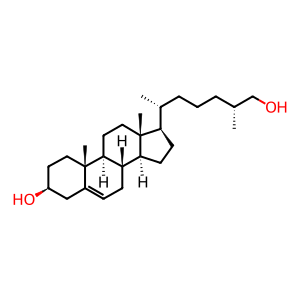
27-hydroxycholesterol binds directly to ESR1 and ESR2 to modulate estrogen signaling in a cell-, tissue-, and gene-specific manner, making it a physiological selective ER modulator (SERM) (Umetani et al, 2007; Nelson et al, 2013; Nguyen et al, 2015). In the context of breast cancer, 27-HC acts as an estrogen agonist, promoting ER-dependent cellular proliferation. The development of resistance to aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer can arise in part through epigenetic reprogramming that activates the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway, elevating 27-HC levels and resulting in constitutive ER alpha activation (Nelson et al, 2013; Nguyen et al, 2015). Note that 27-HC binding to the estrogen receptors likely occurs in the context of a chaperone complex as is the case for estrogens, however this has not been explicitly demonstrated.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
27-OH-CHOL [nucleoplasm]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9038029
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
(25R)-cholest-5-ene-3beta,26-diol
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9038029