Reaction: Mitochondrial AGXT2 tetramer transaminates glyoxylate and alanine to glycine and pyruvate
- in pathway: Glyoxylate metabolism and glycine degradation
Mitochondrial AGXT2 (alanine-glyoxylate transaminase 2) catalyzes the irreversible reaction of glyoxylate and alanine to form glycine and pyruvate (Rodionov et al. 2010). The active form of the enzyme is inferred to be a homotetramer from the properties of the homologous rat protein, which has been purified and characterized in vitro (Tamaki et al.990). Most conversion of glyoxylate to glycine in vivo appears to occur in the peroxisome, catalyzed by AGXT, and the physiological role of the AGXT2 reaction is unclear.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
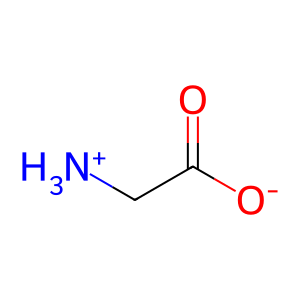
Gly [mitochondrial matrix]
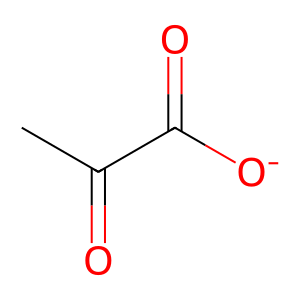
PYR [mitochondrial matrix]
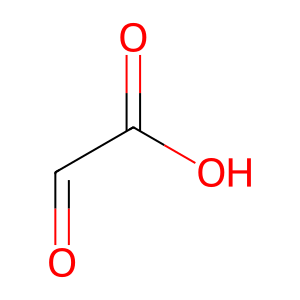
glyoxylate [mitochondrial matrix]
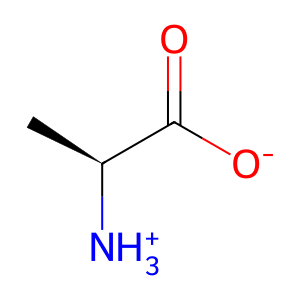
L-Ala [mitochondrial matrix]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-904864
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
glyoxylic acid
L-alanine zwitterion
Reaction output - small molecules:
glycine zwitterion
pyruvate
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-904864