Reaction: GALNTs transfer GalNAc to Mucins to form Tn antigens
- in pathway: O-linked glycosylation of mucins
The family of UDP GalNAc:polypeptide N acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (GalNAc transferases, GALNTs) carry out the addition of N acetylgalactosamine on serine, threonine or possibly tyrosine residues on a wide variety of proteins, and most commonly associated with mucins (Wandall et al. 1997). This reaction takes place in the Golgi apparatus (Rottger et al. 1998). There are 20 known members of the GALNT family, 15 of which have been characterised and 5 candidate members which are thought to belong to this family based on sequence similarity (Bennett et al. 2012). The GALNT-family is classified as belonging to CAZy family GT27. The Tn antigen is the simplest possible amino acid–carbohydrate glycoconjugate and comprises a GalNAc α-O-linked to either serine or threonine. In normal mammalian mucins, GalNAc is substituted by Gal, GlcNAc, or GalNAc forming up to eight different core structures. The unsubstituted Tn antigen is often found in cancer and is associated with poor prognosis (Kamerling 2007).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
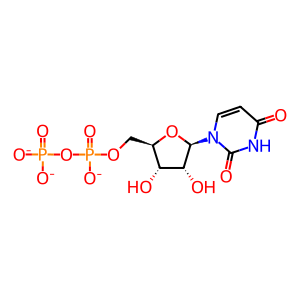
UDP [Golgi lumen]
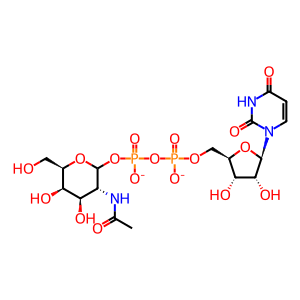
UDP-GalNAc [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-913675
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine(2-)
Reaction output - small molecules:
UDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-913675