Reaction: ABCG2 tetramer transports heme from cytosol to extracellular region
- in pathway: Iron uptake and transport
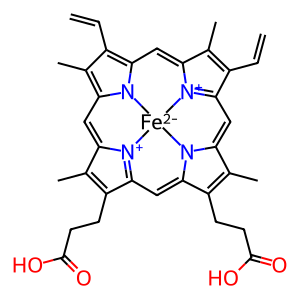
Heme is utilised as a prosthetic group in the production of hemoproteins inside cells. However, when intracellular heme accumulation occurs, heme is able to exert its pro-oxidant and cytotoxic action. The amount of free heme must be tightly controlled to maintain cellular homeostasis and avoid pathological conditions (Chiabrando et al. 2014). The tetrameric efflux pump ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2) (Xu et al. 2004) can relieve cells from toxic heme concentrations even against a concentration gradient. It is expressed in placenta, liver, and small intestine (Krishnamurthy et al. 2004, Doyle & Ross 2003, Zhang et al. 2003).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
heme [extracellular region]
ADP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
heme [cytosol]
Pi [cytosol]
heme [extracellular region]
ADP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
heme [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-917979
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
ferroheme b
water
ATP(4-)
ferroheme b
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ferroheme b
ADP(3-)
hydrogenphosphate
ferroheme b
ADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-917979