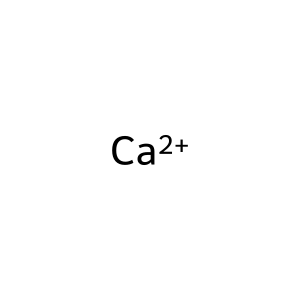Reaction: ATP2C1/2:Mg2+ transport cytosolic Ca2+ to Golgi lumen
- in pathway: Ion transport by P-type ATPases
Accumulation of calcium into the Golgi apparatus is mediated by sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium-ATPases (SERCAs) and by secretory pathway calcium-ATPases (SPCAs). There are two human genes which encode SPCAs; ATP2C1 and ATP2C2 which encode magnesium-dependent calcium-transporting ATPase type 2C members 1 and 2 (ATP2C1 and 2) respectively (Sudbrak et al, 2000; Vanoevelen et al, 2005). Defects in ATP2C1 are the cause of Hailey-Hailey disease (HHD), an autosomal dominant disease characterized by persistent blisters and erosions of the skin (Hu et al, 2000).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
ADP [cytosol]
Ca2+ [Golgi lumen]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-936883
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
ADP(3-)
calcium(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-936883