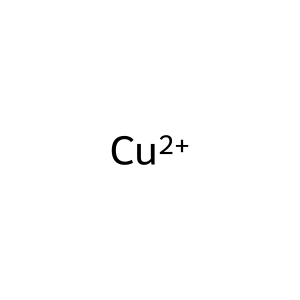Reaction: ATP7B transports cytosolic Cu2+ to Golgi lumen
- in pathway: Ion transport by P-type ATPases
The human gene ATP7B encodes the copper-transporting ATPase 2 (ATP7B, ATPase2, Wilson's protein) which is expressed mainly in the liver, brain and kidneys (Bull et al, 1993). ATP7B resides on the trans-Golgi membrane where it it thought to sequester copper from the cytosol into the golgi (Yang et al, 1997). Defects in ATP7B are the cause of Wilson disease (WD), an autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism characterized by the toxic accumulation of copper in a number of organs, particularly the liver and brain (Thomas et al, 1995).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Pi [cytosol]
Cu2+ [Golgi lumen]
ADP [cytosol]
H2O [cytosol]
ATP [cytosol]
Cu2+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-936895
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
water
ATP(4-)
copper(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
hydrogenphosphate
copper(2+)
ADP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-936895