Reaction: FUT3 transfers Fuc to Type 1 chains to form LeA
- in pathway: Lewis blood group biosynthesis
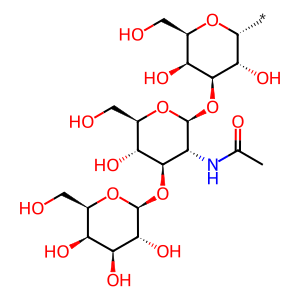
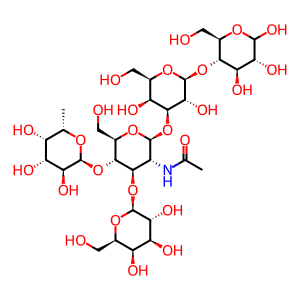
The FUT3 gene (originally named the Le gene) expresses galactoside 3(4)-L-fucosyltransferase present on the Golgi membrane. FUT3 catalyses the α1,4 and α1,3 addition of fucose to Type 1 and Type 2 oligosaccharide chains respectively, thereby playing a role in Lewis blood group determination (Kukowska-Latallo et al. 1990). Here, the addition of fucose to the subterminal N-acetylglucosaminyl (GlcNAc) residue of Type 1 chains in an α1,4 linkage forms the Lewis A antigen (LeA). In Lewis negative (Le(a- b-)) individuals, FUT3 is inactivated by either of two mutations resulting in a single amino acid substitution in the catalytic region (Nishihara et al. 1993). LeA is found on red blood cells (~20%) and in saliva and other secretions (>90%) of Europeans. LeA is a water-soluble antigen and red blood cells acquire Lewis specificity by adsorbing it onto their surfaces from blood plasma.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
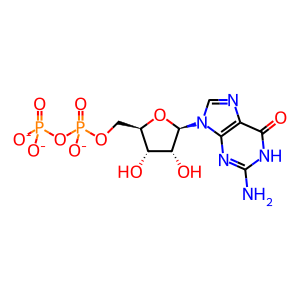
GDP [Golgi lumen]
LeA [Golgi lumen]
Type 1 chain [Golgi lumen]
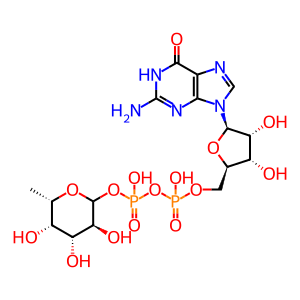
GDP-Fuc [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9603986
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-alpha-D-Gal-yl group
GDP-L-fucose
Reaction output - small molecules:
GDP(3-)
alpha-L-Fucp-(1->4)-[beta-D-Galp-(1->3)]-beta-D-GlcpNAc-(1->3)-beta-D-Galp-(1->4)-D-Glcp
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9603986