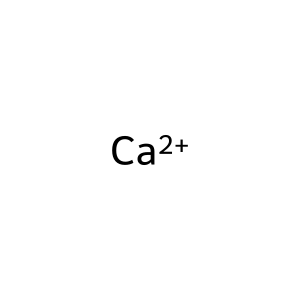Reaction: Calcium binds calmodulin at the synapse
- in pathway: Long-term potentiation
Upon NMDA receptor-mediated increase in calcium (Ca2+) concentration, calmodulin (CALM1, commonly labeled as CaM) is activated by binding to four calcium ions (Crouch and Klee 1980, DeLorenzo 1982). In neurons, CALM1 is concentrated at the synapse by binding to neurogranin (NRGN). After neuronal activation-induced influx of Ca2+, CALM1 dissociates from NRGN and binds to Ca2+ to activate downstream signaling. Dissociation of CALM1 from NRGN may be facilitated by PKC-mediated phosphorylation of NRGN (Zhong et al. 2009).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ca2+ [cytosol]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9618811
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9618811