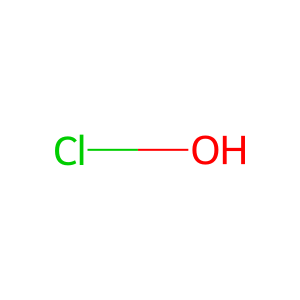
Reaction: Hypochlorous acid (HOCL) oxidizes Cys residues to form Cys-sulfenyl chloride
Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) is a powerful oxidant generated from H2O2 and Cl- by the heme enzyme myeloperoxidase (MPO), which is released from activated leukocytes. HOCl leads to chlorination of thiol-containing cysteine (Cys) residues forming Cys-sulfenyl chloride (Cys-SCl) intermediate and then Cys-sulfenic acid (Cys-SOH), which can either form a disulfide with an adjacent thiol or be further oxidized by HOCl to generate Cys- sulfinic and Cys-sulfonic acids sequentially (Peskin AV & Winterbourn CC 2001; Hawkins CL et al. 2003; Paulsen CE & Carroll KS 2013; Winterbourn CC & Kettle AJ 2013). Disulfides function as redox switches to control protein activity and protect thiol groups against overoxidation to Cys-sulfinic and -sulfonic acids.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
H2O [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
HOCl [phagocytic vesicle lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9625548
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
hypochlorous acid
Reaction output - small molecules:
water
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9625548