Reaction: Addition of GlcNAc to the glycan on the A arm
- in pathway: N-glycan trimming and elongation in the cis-Golgi
This is the first committed step in the synthesis of complex and hybrid N-glycans and is specific to multicellular organisms (Kumar et al, 1990; Hull et al, 1991). Hybri N-glycans are important for inter-cellular interactions and therefore during embryonic development of multicellular organisms, and it is probable that these pathways have evolved just before the emergence of multicellular organisms. Support for this hypothesis is provided by the phenomena of CDG and by the effects of null mutations in C.elegans.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
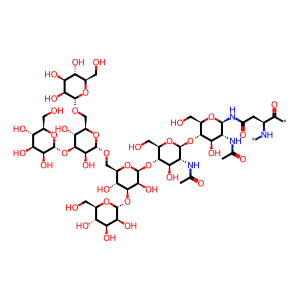
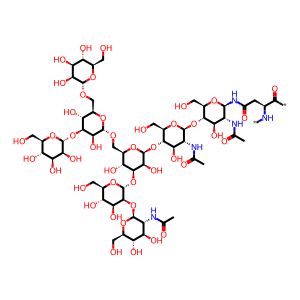
(GlcNAc)3 (Man)5 (Asn)1 [Golgi lumen]
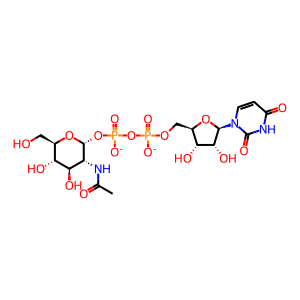
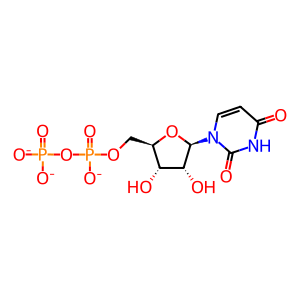
UDP [Golgi lumen]
UDP-GlcNAc [Golgi lumen]
(GlcNAc)2 (Man)5 (Asn)1 [Golgi lumen]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-964768
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
UDP-N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine(2-)
N-{alpha-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-Man-(1->6)]-beta-Man-(1->4)-beta-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-GlcNac}-L-Asn residue
Reaction output - small molecules:
N(4)-{beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->2)-alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->3)-[alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-alpha-D-Man-(1->6)]-beta-D-Man-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)-beta-D-GlcNAc}-Asn residue
UDP(3-)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-964768