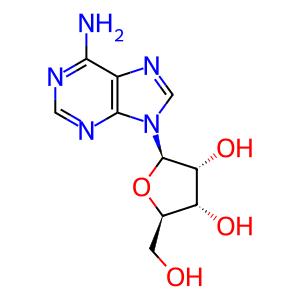
Reaction: ADORA2B binds Ade-Rib
- in pathway: ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production
Adenosine receptors A2a and A2b (ADORA2A and ADORA2B) bind extracellular adenosine (Ado-Rib) and are believed to play a role in regulating myocardial oxygen consumption and coronary blood flow (Peterfreund 1996). The A2A receptor is responsible for regulating myocardial blood flow by vasodilation of the coronary arteries, which increases blood flow to the myocardium, but may lead to hypotension. Just as in A1 receptors, this normally serves as a protective mechanism. A2B receptor work (Pierce KD et al, 1992) has lagged behind research in the other adenosine receptors.
Both ADORA receptors mediate their actions by coupling with the G protein alpha s subunit which activates adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular cAMP concentrations. In surfactant physiology, the receptor:adenosine complex positively regulates surfactant export from lamellar bodies. (Cooper JA et al, 1995; Linden J et al, 1999). Adenosine deaminase (CECR1, ADA2) degrades extracellular adenosine (Ade-Rib), reducing or neutralising the positive regulatory effect of adenosine in surfactant export.
Both ADORA receptors mediate their actions by coupling with the G protein alpha s subunit which activates adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular cAMP concentrations. In surfactant physiology, the receptor:adenosine complex positively regulates surfactant export from lamellar bodies. (Cooper JA et al, 1995; Linden J et al, 1999). Adenosine deaminase (CECR1, ADA2) degrades extracellular adenosine (Ade-Rib), reducing or neutralising the positive regulatory effect of adenosine in surfactant export.
Reaction - small molecule participants:
Ade-Rib [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9660829
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
adenosine
Reaction output - small molecules:
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9660829