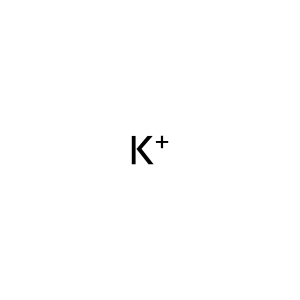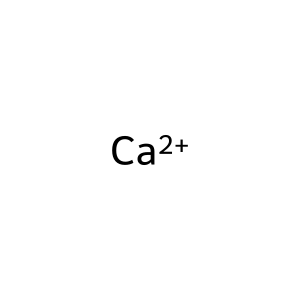Reaction: Mechanoelectrical transduction (MET) channel transports cations into the cytosol of stereocilia of cochlear outer hair cell
The mechanoelectrical transduction (MET) channels located at the tips of stereocilia on the apical surface of outer hair cells (OHCs) are opened by mechanical force exerted on the channels by CDH23:PCDH15 tip links that connect the apices of shorter stereocilia to the sides of taller stereocilia (inferred from mouse homologs). A CDH23 dimer is connected to the cytoskeleton of a taller stereocilium via USH1C (Harmonin), USH1G (SANS), and MYO7A (MYOVIIA) (inferred from mouse homologs). By a calcium-dependent interaction, a CDH23 dimer on the side of a taller stereocilium is bound to a PCDH15 dimer connected to a MET channel on the apex of a shorter stereocilium (inferred from mouse homologs). The MET channel complex contains at least TMC1 or TMC2, TMIE, CIB2, and LHFPL5, with which PCDH15 interacts (inferred from mouse homologs). Deflection of the stereocilia by sound causes increased tension on CDH23:PCDH15, resulting in an increased probability of the open state of the MET channel. The MET channel is relatively non-specific for cations and conducts calcium ions and potassium ions from the extracellular scala media into the cytosol of the OHC. Depolarization of the OHC results in shortening of the OHC due to a change in conformation of SLC26A5 (prestin) located in the lateral membrane of the OHC. The composition of the cytoskeleton of OHCs differs from that of inner hair cells (IHCs): MPP1 and GSN are present in OHCs but absent from IHCs (inferred from mouse homologs).
Reaction - small molecule participants:
K+ [cytosol]
Ca2+ [cytosol]
K+ [extracellular region]
Ca2+ [extracellular region]
Reactome.org reaction link: R-HSA-9663363
======
Reaction input - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
calcium(2+)
Reaction output - small molecules:
potassium(1+)
calcium(2+)
Reactome.org link: R-HSA-9663363